Education
 The epatitis C virus, commonly known as the Hep C virus, left unchecked in the bloodstream, often leads to a disease called hepatitis that affects condition and function of the liver.
The epatitis C virus, commonly known as the Hep C virus, left unchecked in the bloodstream, often leads to a disease called hepatitis that affects condition and function of the liver.
Harvoni is a polymerase inhibitor used to treat patients infected with Genotype 1 and 4 of Hepatitis C. The treatment can be administered to patients coinfected with the HIV virus and suffering from liver cirrhosis. In some cases this medicine has been used successfully to treat patients that cannot be treated with therapies of interferon.
It is important to say that this treatment has been broadly proved in its efficacy and safety. The medicine has been evaluated in six different studies with almost 2,000 participants.
The components of
Harvoni generic the Sofosbuvir and Ledipasvir
fight some proteins that facilitate the reproduction of the virus thus suppressing the progression of it and giving the opportunity to the patient to heal the liver.
 The Hepatitis C virus is believed to be exclusively transmitted via the blood. The virus can transmit when the blood of an uninfected person gets in contact with the blood of an infected person.
The Hepatitis C virus is believed to be exclusively transmitted via the blood. The virus can transmit when the blood of an uninfected person gets in contact with the blood of an infected person.
Hep C transmission is most likely to happen when the blood of an infected person comes in direct contact with the blood of an uninfected person such as in blood transfusions improperly screened, the shared use of needles among illicit drug users, accidental needle sticks with infected blood, and direct blood to blood contact with an infected person’s open wound.
 Today many new single or multiple entity medications are showing a very good success rate in the “cure” of the Hep C virus.
Today many new single or multiple entity medications are showing a very good success rate in the “cure” of the Hep C virus.
Only your doctor can offer the best opinion in deciding which medications(s) you should be prescribed and for how long.
In general, the odds of a “cure” depends of many factors, the most important of them being which Hep C genotype you are infected with, the viral load at the moment you initiate therapy, your past experience with other treatments tried, if any, the degree of your liver damage, whether you are a liver transplanted person or you are waiting for a liver transplant, and the ability of your body to tolerate the treatment prescribed.

People born between1945-1965 are 5 times more likely to be infected with the Hep C virus.
Of all people currently diagnosed with the virus, 75% of them were born during those years.
Hepatitis C infection is the leading cause of liver cancer and the number one reason for liver transplantation in USA
 Hepatitis caused by the hepatitis C virus is a disease of the liver that can last for a very long without treatment.
Hepatitis caused by the hepatitis C virus is a disease of the liver that can last for a very long without treatment.
The Hep C virus can cause different kinds of damage to a person’s liver that is infected.
In the short term, virus damage caused by the Hep C virus usually produces fibrosis and can sometimes later cause mild scarring of the liver. As time passes with an infected and untreated liver, the risk of cirrhosis, a severe form of liver scarring, increases and causes many debilitating symptoms. Finally, an untreated infected liver may see the appearance of cancer, may result in liver failure, and may unfortunately lead to death.
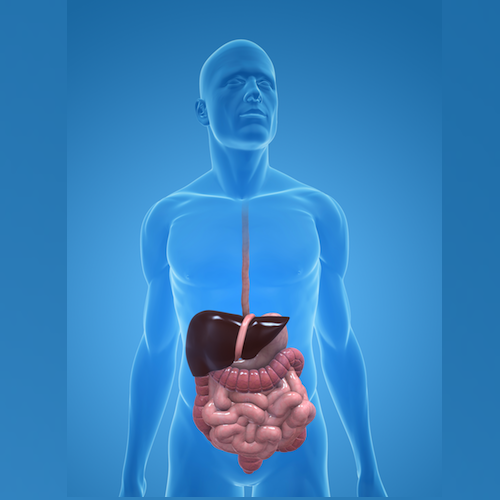 The liver is one of the most vital and important organs of the body and among its functions are:
The liver is one of the most vital and important organs of the body and among its functions are:
The early stages of the hepatitis are called acute, they can be mild or severe. When the hepatitis last for more than 6 months it is called chronic.
Hepatitis A and E do not reach chronic stages. All other Hepatitis B,C, and D can become chronic, and B and C are especially serious when they last for more than six months.
Many types of Hepatitis virus have been identified:
First of all, is important to say that a Hep C viral infection does not easily spread from one person to another. Research has show that the most likely cause of transmission is blood to blood contact, thus the risk of becoming infected without first having contact with infected blood is extremely low.
You can take the following prevention measures to minimize the risk of becoming infected:
- Never share injection needles with anyone.
- If you are at risk of being exposed to another person’s blood or open wound, always use latex gloves.
- Follow safe sex practices that will keep you from becoming in contact with another person’s blood. Consider using condoms.
The virus can be classified into six different genotypes and each one divided into many subtypes.
A genotype is a classification made based on the RNA (its gene structure) of the Hep C virus.
Usually a person is infected only with one type of virus genotype. Clearly identifying the type of Hep C virus genotype a person is carrying is critical for the doctor to know in advance in order for him or her to prescribe the right course of prescription medication therapy.